Table of Contents
Even minor blending inaccuracies can affect production timelines, product quality, and overall efficiency in the complex environment of oil and gas refineries. These issues may lead to reblending, product giveaways, or non-compliance penalties, resulting in significant operational costs. What strategies can help improve blending accuracy in such conditions? This article outlines common challenges in refinery blending and examines how hybrid systems—particularly those that incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive modeling—are being used to enhance accuracy and support more reliable outcomes.
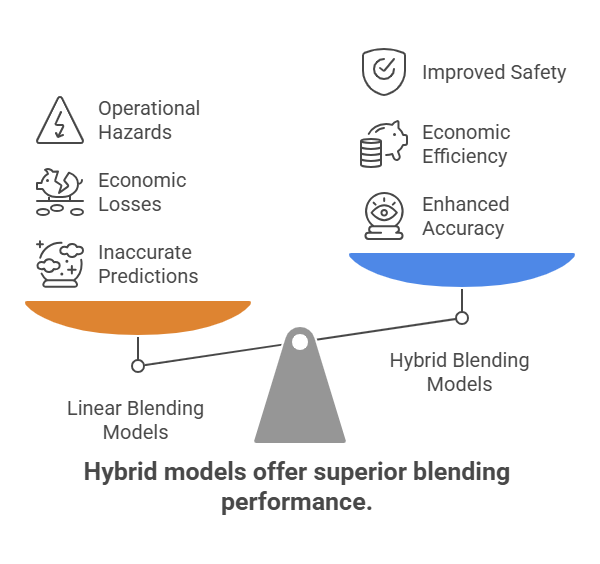
Blending Errors from Incorrect Component Ratio Predictions
Blending crude and refined products involves nonlinear behavior. Traditional blending models frequently rely on linear assumptions, which often do not reflect actual process dynamics. Though commonly used, linear programming (LP) or rule-based models are limited in handling complex interactions within multi-component blends.
- AspenTech has reported that such limitations can lead to a 3–5% blend giveaway due to inaccurate ratio estimations. Furthermore, inaccurate blend ratio predictions can present process safety risks.
- According to the American Institute of Chemical Engineers’ Center for Chemical Process Safety (AIChE CCPS), deviations from expected blend compositions may elevate the likelihood of operational hazards, including high-pressure incidents and off-specification products.
- To address these issues, hybrid models that combine LP with first-principles and machine learning (FPBM) methodologies are increasingly being implemented.
- Offsite Management Systems (OMS) has documented that FPBM-AI models offer over a 15% improvement in predictive accuracy over LP-only systems, enhancing reliability and reducing product giveaways.
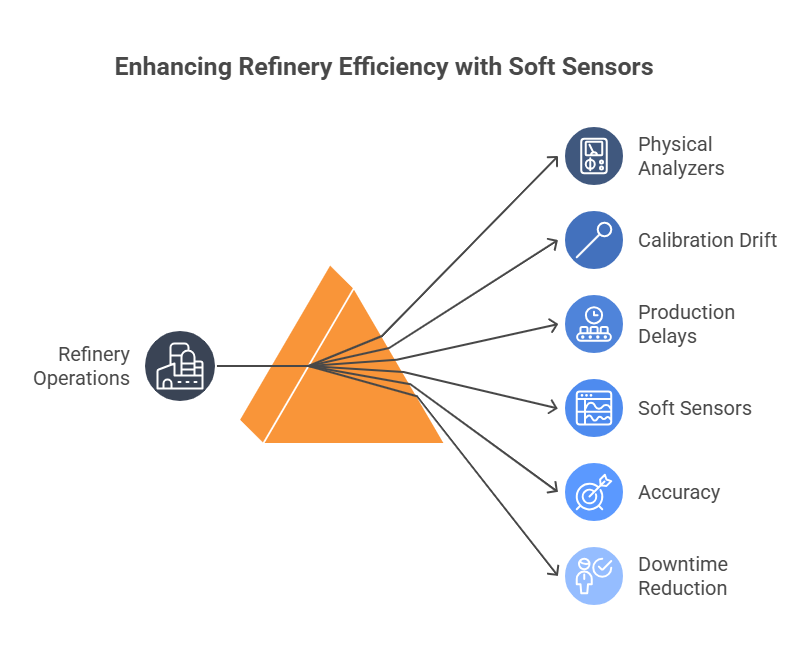
Blending Errors Due to Inadequate Analyzer Coverage or Failure
Physical analyzers, such as those developed by Honeywell and Emerson, are critical to ensuring that blends meet required specifications for parameters such as sulfur content, octane number, and viscosity. However, analyzers can malfunction or drift out of calibration over time, particularly under prolonged use or harsh environmental conditions. Such failures can delay blend approvals by one to four hours, with estimated losses exceeding $10,000 per hour due to production hold-ups.
- Many refineries have adopted soft sensors—virtual analyzers trained using historical and real-time operational data to address these vulnerabilities.
- These virtual systems can provide near-real-time estimates for critical properties with a typical accuracy of ±0.1%.
- OMS has incorporated these sensors into its blend monitoring systems, reducing dependency on physical analyzers and minimizing associated downtime.
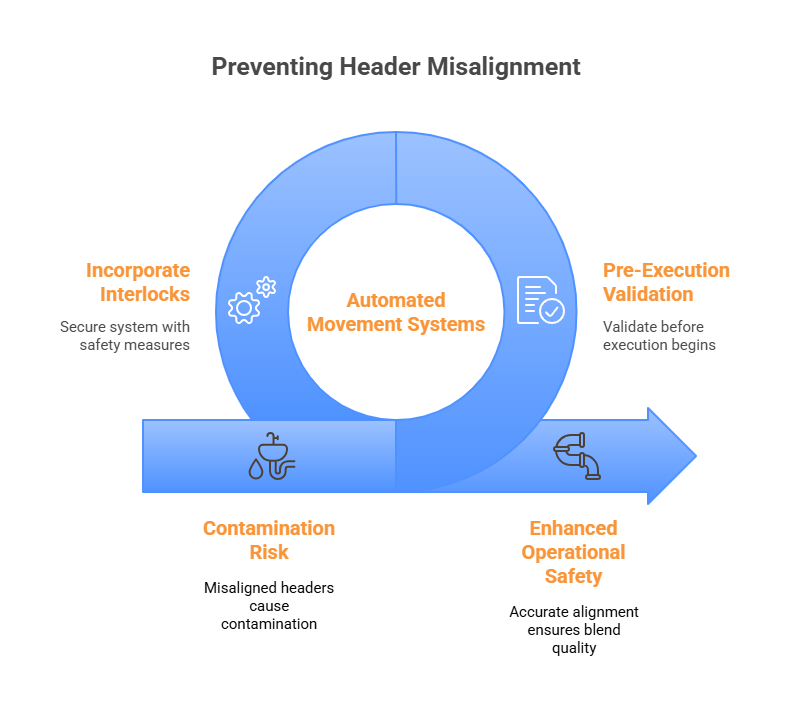
Blending Errors from Poor Blend Header Line-Up and Switching
Properly aligning and sequencing the blend headers is key to maintaining product quality. A mistake in the header line-up or switching process can cause cross-contamination, sometimes severe enough to require reprocessing or discarding entire batches. That’s why industry standards, like those from the International Society of Automation (ISA), stress the need for strong control systems to help prevent these kinds of errors.
- The ARC Advisory Group has reported that a single header contamination incident can result in the loss of 1,000–5,000 barrels, depending on the product, and can significantly impact downstream operations.
- OMS’s automated movement systems include pre-execution validation and interlocks, which help ensure correct header configurations, reduce the potential for errors, and enhance operational safety.
Blending Errors Linked to Tank Heel Mismanagement
The residual product—the tank heel—remaining in tanks post-discharge can affect subsequent blends if not correctly managed. According to the American Petroleum Institute (API), failure to account for tank heel volumes can lead to blend quality deviations of up to 1%.
- Emerson has observed that tank heel estimations are frequently based on static or outdated calculations that may not consider real-time variables such as temperature stratification or operator changes.
- OMS integrates advanced heel modeling into its blend simulation and volume calculations, promoting accurate tracking and minimizing blend quality variability.

Blending Errors from Manual Adjustments Without Simulation
When performed without real-time simulation, manual interventions during blending can introduce significant operational risk. AVEVA notes that manual flow changes, if not verified through simulation, can result in blends falling outside specification limits.
- Case studies from ControlGlobal illustrate instances where single manual overrides have led to blend failures, resulting in financial losses exceeding $150,000 per tank.
- OMS offers online simulation tools that continuously assess blend predictions as operator inputs change. This allows for proactive risk management and reduced reliance on manual corrections.
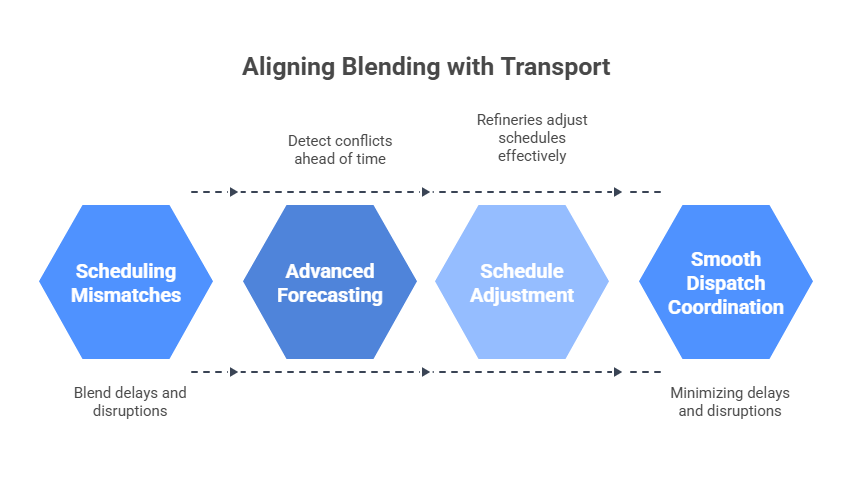
Blending Errors from Scheduling Mismatch and Dispatch Interruptions
Coordinating blending activities with dispatch logistics is essential to maintaining refinery throughput. Misalignment between blend schedules and transport availability can result in inventory buildup, delayed deliveries, and customer dissatisfaction. ABB reports that even advanced model predictive control systems may struggle to align blend readiness with dispatch schedules.
- According to a KBC survey, scheduling mismatches account for more than 25% of blend delays.
- OMS addresses this with forecasting and simulation tools that identify and flag potential conflicts 6–12 hours in advance, allowing for timely adjustments and smoother dispatch coordination.
Conclusion: Smarter Blending Begins with Smarter Systems
As the refining sector faces increasing operational, environmental, and economic pressures, advanced AI/ML-based systems are becoming indispensable tools. McKinsey and other industry leaders have emphasized the growing importance of data-driven automation in maintaining competitiveness and safety.
Offsite Management Systems (OMS) exemplifies this industry shift with its integrated suite of solutions, which includes FPBM-based blend optimization, virtual sensor analytics, and predictive scheduling tools. Documented outcomes include:
- $1.8 million per year in blend margin improvements at a Latin American refinery due to reduced reblends
- $500,000 in capital expenditure savings through virtual analyzer implementation
- 95% reduction in manual blend interventions within the first three months of deployment
These results underscore the value of transitioning from legacy systems to comprehensive, intelligent blending platforms. Rather than relying on incremental upgrades, the industry’s path forward lies in adopting robust, integrated technologies that enhance safety, accuracy, and operational efficiency.






